Airplane Parts Diagram: A Comprehensive Guide to Aircraft Components
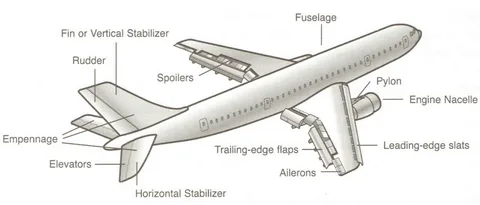
Understanding the various parts of an airplane parts is essential for anyone interested in aviation, whether you’re a student, a hobbyist, or a professional in the field. This comprehensive guide will explore the key components of an aircraft, providing detailed explanations and a clear diagram to help you visualize and understand each part’s function.
Fuselage: The Main Body
The fuselage is the central body of the airplane, housing the cockpit, passenger cabin, and cargo hold. It provides structural integrity and connects all other parts of the aircraft.
Cockpit
The cockpit is where the pilots control the aircraft. It contains all the necessary instruments and controls for flight operations.
Passenger Cabin
The passenger cabin is the area where passengers sit during the flight. It includes seating, restrooms, and often, an in-flight entertainment system.
Cargo Hold
The cargo hold is the section of the fuselage where luggage and other cargo are stored.
Wings: Lift and Stability
The wings are crucial for flight, providing the lift needed to keep the airplane airborne. They are designed with an airfoil shape to create a pressure difference between the upper and lower surfaces.
Ailerons
Ailerons are hinged surfaces located on the trailing edge of the wings. They control the aircraft’s roll and help in making turns.
Flaps
Flaps are also located on the trailing edge of the wings. They can be extended or retracted to change the wing’s shape, aiding in takeoff and landing by increasing lift at lower speeds.
Empennage: Tail Assembly
The empennage, or tail assembly, includes several components that help stabilize the aircraft and control its pitch and yaw.
Horizontal Stabilizer
The horizontal stabilizer is a fixed wing section on the tail that provides stability in the pitch axis, preventing the nose from pitching up or down.
Elevator
The elevator is a movable surface on the horizontal stabilizer that controls the pitch, allowing the nose to move up or down.
Vertical Stabilizer
The vertical stabilizer is the fixed section of the tail that provides stability in the yaw axis, preventing the nose from swinging left or right.
Rudder
The rudder is a movable surface on the vertical stabilizer that controls yaw, allowing the nose to move left or right.
Engines: Power and Thrust
Engines are the powerhouse of the airplane, providing the thrust needed for takeoff, flight, and landing.
Jet Engines
Jet engines are commonly used in commercial and military aircraft. They work by compressing air, mixing it with fuel, and igniting the mixture to produce high-speed exhaust gases that propel the airplane forward.
Propeller Engines
Propeller engines are typically found on smaller aircraft. They use a propeller to generate thrust by pulling or pushing air backward.
Landing Gear: Takeoff and Landing
The landing gear supports the airplane during takeoff, landing, and while it is on the ground.
Main Gear
The main gear is the primary set of wheels located near the airplane’s center of gravity. They bear most of the aircraft’s weight during landing and takeoff.
Nose Gear
The nose gear is the set of wheels located at the front of the aircraft. It helps steer the airplane on the ground.
Avionics: Navigation and Communication
Avionics encompass the electronic systems used for navigation, communication, and monitoring the aircraft’s performance.
Flight Instruments
Flight instruments provide pilots with crucial information about the aircraft’s altitude, speed, heading, and attitude.
Navigation Systems
Navigation systems help pilots determine the aircraft’s position and plot a course to the destination. These systems often include GPS, inertial navigation systems, and radio navigation aids.
Communication Systems
Communication systems enable pilots to communicate with air traffic control and other aircraft, ensuring safe and coordinated flight operations.
Fuel System: Powering the Flight
The fuel system stores and delivers fuel to the engines. It includes fuel tanks, pumps, filters, and fuel lines.
Fuel Tanks
Fuel tanks are strategically located in the wings and fuselage to distribute weight evenly and maintain balance.
Fuel Pumps
Fuel pumps transfer fuel from the tanks to the engines, ensuring a steady flow at the required pressure.
Fuel Filters
Fuel filters remove impurities from the fuel before it reaches the engines, preventing clogs and ensuring efficient combustion.
Conclusion: The Complexity of Aircraft Components
An airplane is a marvel of engineering, with each component playing a crucial role in ensuring safe and efficient flight. By understanding the different parts of an aircraft and their functions, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and ingenuity of aviation design.
This guide provides a detailed overview of the key components of an airplane. Whether you’re studying for an exam, working on a project, or simply curious about aviation, this comprehensive guide will help you understand the intricate workings of aircraft components.